Causes of Social Media Addiction
Social media platforms are designed to elicit excessive dopamine releases from users through likes, comments, and increasing follower numbers. These platforms play on humans’ natural reward system, which has caused many teens and young adults to develop addictions to using social media.

 Written and edited by our team of expert legal content writers and reviewed and approved by Attorney Matthew Bergman
Written and edited by our team of expert legal content writers and reviewed and approved by Attorney Matthew Bergman
- Content last updated on:
- February 10, 2026
Written and edited by our team of expert legal content writers and reviewed and approved by

- Content last updated on:
- February 10, 2026
Tweens, teens, and young adults are easy targets for the social media industry, which intentionally creates addictive platforms at their expense. The attorneys at the Social Media Victims Law Center are dedicated to helping parents hold these companies accountable and restore the lives of their teens.
What is addiction?
Addiction is a disorder of the brain’s reward system, characterized by a powerful craving or compulsion that is so strong the person will stop at nothing to engage in the activity, regardless of the negative consequences.
How the Reward System Works
The brain’s reward system releases dopamine to reward an individual with pleasure when certain activities are performed that the brain perceives as necessary for survival. Dopamine is a powerful neurotransmitter that helps create this pleasure response and targets the decision-making center of the brain.
The brain’s reward system can be activated during any pleasurable activity. The more an activity is repeated, the more it becomes ingrained in the brain’s neural circuitry as a necessary activity.
The reward system subsequently compels the individual to seek out the activity in the same way it compels one to eat. The executive center of the brain is programmed to seek out the behavior no matter what the cost.

Withdrawal
The body develops a tolerance to dopamine, resulting in a need for higher dopamine levels in order to experience pleasure. The compulsion to continue seeking the substance becomes a matter of survival rather than pleasure.
When the activity is stopped, intense cravings occur, and the individual can no longer experience pleasure from ordinarily pleasurable activities.
As a result of these chemical changes in the brain’s reward system, behavioral addictions like social media addiction are physically as well as psychologically addictive. Withdrawal symptoms for substance abuse and behavioral addictions are similar and may include agitation, irritability, difficulty sleeping, and personality changes.
What makes social media addictive?
Social media apps are addictive by design. They receive increased advertising revenue as users spend more time on their respective platforms. They use the Fogg Behavioral Model to turn casual social media use into a habit by implementing the following three-pronged approach, which perfectly mirrors the addiction process:
- Motivation
- Anticipation teens feel about getting likes, comments, or posts
- Fear of missing out (FOMO)
- Action
- The physical act of reading and responding, such as liking or commenting
- Trigger
- The circumstance that activates the motivation, such as a phone vibrating when a notification is received
Adolescent Development
Adolescence is the challenging transitional period between childhood and adulthood when parental influence decreases and peer influence becomes more important. During adolescence, peer acceptance and a sense of belonging are highly prioritized.
Adolescents are sensitive to rejection and acceptance. They experience strong emotionality and impulsivity. Being accepted or rejected on social media has quantifiable impacts on brain activity and development.
Factors That Keep Young People Hooked
Understandably, these factors make adolescents more susceptible to forming risky habits that can trigger the addictive cycle, such as mindlessly scrolling and constantly checking notifications and likes. This behavior is driven by the following factors:
- Fear of missing out (FOMO) – A strong fear triggered by notifications or periods of lack of access to social media, in which a teen believes they may be missing updates, with an underlying fear that one of the following consequences will occur:
- They will let someone down by not responding immediately
- They will lose their social standing
- They will miss out on an invitation or something fun
- They will be left out of important conversations
- The need for a security blanket to deal with loneliness, awkwardness, or anxiety
- The desire to self-medicate underlying issues such as depression or boredom
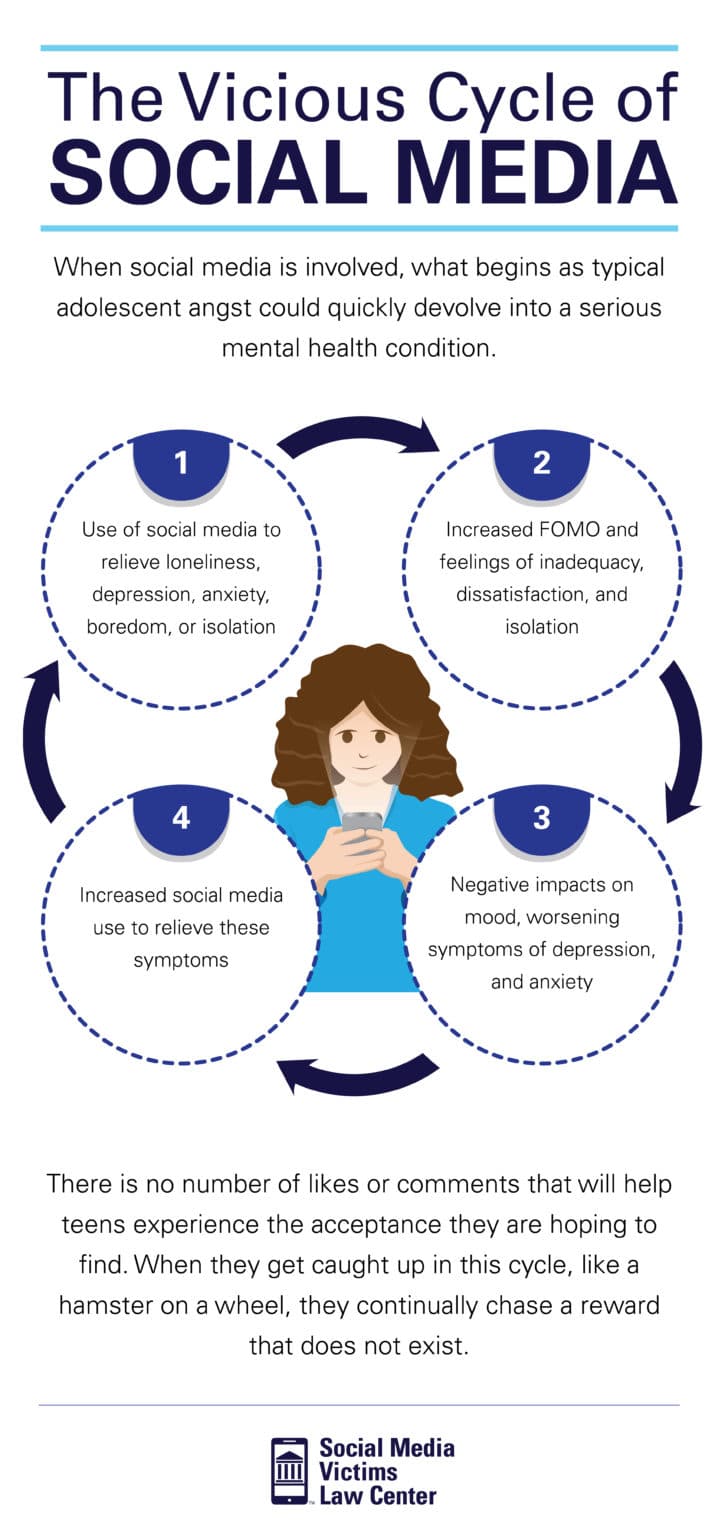
The Vicious Cycle
When social media is involved, what begins as typical adolescent angst could quickly devolve into a serious mental health condition.
- Use of social media to relieve loneliness, depression, anxiety, boredom, or isolation
- Increased FOMO and feelings of inadequacy, dissatisfaction, and isolation
- Negative impacts on mood, worsening symptoms of depression and anxiety
- Increased social media use to relieve these symptoms (and the cycle continues)
There is no number of likes or comments that will help teens experience the acceptance they are hoping to find. When they get caught up in this cycle, like a hamster on a wheel, they continually chase a reward that does not exist.
Risk Factors for Addiction to Social Media
Spending too much time on social media is a risky venture for any teen. However, some teens are especially at risk of becoming addicted.
- Female gender – While boys are more likely to become addicted to gaming, girls are more likely to gravitate toward social media.
- Low self-esteem – Teens with low self-esteem are more likely to be uncomfortable with face-to-face interactions and use social media as an escape.
- Depression and anxiety – These emotions commonly increase as a result of face-to-face and online social interactions. This increases the likelihood of teens escaping into social media, especially for those with social anxiety.
- Impulsivity and disinhibition – Poor impulse control and sensation-seeking lead teens to do whatever feels good at the moment without regard for consequences, making them vulnerable to addictions in general.
- Poor body image – Poor body image is most prevalent in girls, who often post edited, idealized images of themselves. Any resulting positive feedback fosters addiction as these girls live vicariously through their idealized selves on social media.
- Extraversion – Extraverts tend to establish more social connections online.
- Introversion – Introverted teens tend to be more passive online, liking and commenting on existing posts rather than starting their own. This is often a reflection of their offline difficulties initiating relationships.

Tips to Prevent Social Media Addiction
The brain reward system is highly active in teens, and self-control is generally not developed until around the age of 21. Preventing social media addiction in teens requires measures that prevent the activation of the reward system. The following measures can help:
- Establish a positive, open dialogue about social media usage with your teen and discuss the dangers of addiction.
- Establish a family media plan that limits when social media is accessed and for how long.
- Set a good example by following the same guidelines for social media use that you set for your child.
- Require your child to leave notifications turned off. Your child can check notifications during their allotted social media time. Every notification sound or vibration is a potential brain reward system trigger. In addition to preventing the addiction cycle, this accomplishes the following:
- Establishes healthy social media habits early
- Prevents the development of FOMO
- Prevents constant distractions
If Your Child Has Been Harmed by Social Media
Our compassionate attorneys are dedicated to helping victims stand up to large companies who cause harm because of negligence and greed. Contact us today if your child has been harmed by social media.
Frequently Asked Questions
For individuals and children who have been
We only handle cases on a contingent fee basis. This means that we are paid a portion of any recovery obtained in the case and you do not owe us any attorneys’ fees if the lawsuit does not result in a recovery.
Every case is unique. Our attorneys will work with your family to evaluate your potential case and help you evaluate whether filing a lawsuit or other legal proceeding is in your family’s best interest. Generally speaking, the types of cases we handle involve serious mental health effects, including attempted or completed suicide, eating disorders, inpatient mental health treatment, or sexual trafficking/exploitation that was caused by or contributed to through addictive or problematic social media use by teens and young adults.
We are a law firm based near Seattle, WA comprised of lawyers who have spent their entire careers representing victims who have been harmed by dangerous products. We are also parents. Shocked and troubled by the recent revelations about the harm caused to teens and young adults by social media platforms, which powerful technology companies have designed to be highly addictive, Social Media Victims Law Center was launched specifically to help families and children who have suffered serious mental harm or exploitation through social media use to obtain justice.
Your Child's Experience Matters, and Their Story Could Make a Difference
Related Pages
Client Testimonials
Is Your Child Addicted to Social Media?
You Are Not Alone.
We have helped hundreds of families just like yours whose children and teens were affected by social media addiction.
Explore Popular Topics

Addiction

Suicide

Eating Disorders

Anxiety

Bullying

Sexual Abuse

Body Image


